What Is Cloud Computing? The Benefits Explained…

The concept of ‘the cloud’ is older than you think. When it comes to business continuity and ease of collaboration, the idea of cloud infrastructure has helped large and small businesses alike keep on top of a fast-paced, ever-changing world – for many years now.
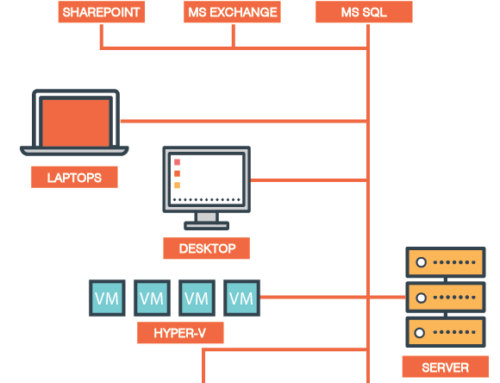
Physical servers and storage space, while still immensely important in day to day running, are becoming more and more obsolete with the emergence of virtual machines. But what are cloud applications, and the different types of computing? Could a private or public cloud service help to boost efficiency, productivity and reliability for your own enterprise?
In the post-pandemic age, there will be a further shift towards remote, floating IT management. Therefore, this model is being sought as a standard to follow.
In this guide, we will take a look into why and how cloud solutions could benefit you, your team, and your public for years to come. Could you be relying on physical hardware and networking when a seamless, streamlined data-based service is the way forward?
What is a cloud computing service?
Cloud platforms deliver essential business services to businesses via the internet. For the average business owner, cloud adoption refers to moving away from physical operating systems and storage – towards virtual servers and an underlying infrastructure based wholly online.
Crucially, cloud providers allow businesses to operate without the need for an outdated, physical environment. As you may imagine, whether for development environments or for customer service providers, this can lead to near unlimited scalability.
Essentially, cloud services are online services – from storage, to servers, to security and analytics. A service provider may offer different options on a subscription basis, too, that business owners can adopt ad hoc.
Access to resources via the cloud means that businesses can essentially set up, scale up and recover at any time, and in any place.
Who uses the cloud?
Software applications, virtual servers and storage solutions available through cloud service providers are used by the vast majority of modern businesses.
Statistics show that up to 94% of enterprises operating globally are using a type of cloud-based computing in one shape or another. What’s more, an average of five different types of cloud technology are used by said businesses.
Cloud services and resources can be used across a wide variety of industries and business standards. For example, the scalability of the cloud can be used in software development, customer
service, or deployment of computing resources to consumers.
The average cloud user does not necessarily use it for business, either. Big brands such as Dropbox, Microsoft Azure and Google Suite all offer cloud computing service standards perfect for the private individual. The average smartphone user, too, may make use of iCloud storage and apps, too, from day to day.
Altogether, cloud environments and cloud systems are hardly new or unusual. That said, there are more than a few key benefits to using cloud computing, which we will cover in more detail below.
How cloud computing works
Cloud servers, storage and software solutions work much like any other web-based service. A cloud vendor will provide an online, virtual interface for business users to log into and access remotely.
Essentially, services such as the Google Cloud platform allow users to access remote servers and systems based completely off-site. A third-party cloud service provider will offer mobile access to CRMs, document recovery / disaster recovery and other virtual resources through one simple login.
Cloud providers compute resources away from the user’s physical operation. This means that there is no need for physical server or storage setup in the office or premises, which would otherwise use an abundance of computing power, and would drive up costs extensively.
Types of cloud services
There are three generic types of cloud service available to users, all of which are available on an as- needed basis.
SaaS (Software as a service)
A SaaS cloud landscape is one that’s available on subscription. Cloud solutions, software and hardware are completely managed by the cloud provider, and the user logs in as and when they need to. This also allows for scalable packages.
IaaS (Infrastructure as a service)
IaaS is a simple cloud computing model that allows users to hire virtual machines, networking, servers and more. This is an ad hoc service, however, users have full control for the rental period.
PaaS (Platform as a Service)
PaaS service models largely target developers working to create and manage application software.
PaaS cloud solutions provide on demand software development standards that takes away the need for users to handle the software maintenance themselves.
Types of cloud
Just as there are different types of cloud vendor service, there are different types of cloud setup, too.
Public cloud
A public cloud service or architecture is completely owned and operated by the cloud vendor. For example, IBM Cloud or Microsoft Azure offer public cloud solutions that users can access from anywhere, but they still own the hardware and oversee the general running.
Private cloud
Private cloud solutions give power to the business or user. Running private cloud services means actively operating the system in-house. However, third party service providers can still host to help free up maintenance demands. The private cloud environment is perfect for those businesses who do not wish to share their processing or running with any other user.
Hybrid cloud
The hybrid cloud service brings together the best of both the public cloud model and the private standard. Crucially, a hybrid cloud model provides a bridge between public and private, enabling a smoother sharing of data and resource procurement across one single model.
What are the benefits of cloud computing for businesses?
It’s pretty safe to say that there are lots of advantages of cloud computing – where it’s complete premises infrastructure or ad hoc data storage off-site, it can do a lot of the heavy lifting for your business. Here are just a few of the biggest benefits to using public cloud providers and otherwise.
Reduced IT costs
The cloud computing infrastructure immediately cuts the cost of running servers and storage in- house. With a SaaS model, businesses can simply pay for the solutions they want and need as and when they desire.
There is also the factor of time savings equalling cost savings, too. Money lost through slow operation, with software and server solutions being streamlined via cloud offerings, can be almost instantly recouped.
Money lost through service downtime is also recouped, as teams working on servers and networks outside of the in-house user can ensure everything is ticking over. The cost savings in comparison with hiring an in-house IT team are likely to escalate – particularly as there is no need to pay for additional training or hiring, either.
Flexible working
The very definition of cloud computing hides the key to its flexibility – it’s floatable, meaning that especially through SaaS, users can log in and access their resources anywhere in the world with a data connection.
This is especially appealing to businesses who are moving more towards a home or flexible working model post-pandemic.
Everyone literally works to the same page when connected via the cloud. This can ensure for a clearer funnel of work and communication, whether on mission critical projects or on day to day tasks and queries.
Access to automatic updates
Perhaps one of the more overlooked assets to private and public cloud computing is the fact that there is very little need to manually maintain or ‘fix’ updates and patches to software and servers.
Many of us have experienced issues in private computing where there is a need to update an operating system, or to increase file storage space. This is largely a process that requires manual
override. Through cloud-based computing, however, solutions to such issues can be delegated and automated with ease.
One of many security measures cloud users will find immediately beneficial is the introduction of automated updates and patching. It’s a time-saving measure that, again, helps to keep things flexible and streamlined.
Additional storage
We will cover scalability in a little more detail across the board below. However, as a business scales, the need for more storage increases, too. Data is growing at an exponential rate, far beyond many people’s comprehension. It will never stop growing, and therefore, it pays for businesses to ensure they have enough storage on hand to accommodate it.
Extra storage in-house can be limited, and at the same time, expensive. The best value storage solutions are those that can scale up and compress down, as per those available in the cloud. It is another clear reason why ambitious companies have long since moved towards the wide open standard.
Smart disaster recovery and business continuity
A leading cloud computing provider will also be able to provide an insight into data protection and recovery. When working with physical in-house files and data, there is always a risk that sensitive information goes awry, gets deleted, or even falls into the wrong hands.
As a result, smarter disaster recovery with cloud security in place means that businesses can bounce back quickly from even the biggest of issues. Natural disasters and company-wide shockwaves can sometimes lead to data getting deleted or lost with ease.
The best resources on the cloud allow you to automatically back up and retrieve data at immediate checkpoints. It’s all based in storage space beyond your office, too.
Scalability
With near-infinite storage space and near-unlimited server and processing potential comes, of course, immense scalability. In a business ecosystem where enterprise owners find they need to pivot and adapt their running frequently, scaling up and down can be difficult.
For the average SME, scaling up would traditionally require investing in an immense array of storage, physical hardware, networking, control solutions and more. It may have even required investing in additional office space to house servers and large scale equipment.
With the cloud, business users can simply take advantage of multiple new solutions and hardware as and when they need to, within the limitations provided by major cloud providers. A public cloud environment, for example, can easily scale up to near unlimited extent, depending entirely on the growing and evolving business needs of the user.
Ease of collaboration
A private or public cloud solution can help users and team members collaborate more freely on complex projects and demands. By streamlining the workforce to log into a SaaS model, for example, a company can provision resources, software versions and relevant data across multiple workstations and access points.
Once again, it is a matter of broad network access. Whether it is disparate mobile device access or in-house, internal users can simply log into the same interfaces and profiles to access all the data and tools they require to finish the job.
With increasing unpredictable demands, a business should be in a position to help make solution finding all the more accessible. This, again, is where central servers and a flat plateau of software and documentation can come in extremely handy.
More processing power
Whether B2B, financial services or otherwise, a business that is scaling up in the modern age is always likely to benefit from additional processing power. That is not always so simple to come across in-house, for reasons already mentioned – costs, space available, and more besides.
For exceptional value, business owners can therefore access computing power to scale up and
down outside of the office. What’s more, this power is fully maintained and managed by experts in the field. There is simply no learning curve.
Additional security
Whether it is a multi cloud operation or otherwise, security can only increase through the deployment of off-site measures.
Cloud security measures can, as mentioned, help to protect data and sensitive documentation in the event of an emergency. Not only that, but those operators running servers and storage solutions off-site will always ensure that they are running at peak security as well as efficiency.
Once again, it is a further measure that takes additional stress away from business operators – and those who may not necessarily know the right steps to take.
Machine learning possibilities
With advances in multi cloud operations comes a steady investment in artificial intelligence and machine learning. The largest of providers in the field are already experimenting with AI and the cloud to offer automation beyond the likes of which we’ve seen thus far.
Machine learning potential allows for even greater efficiency in computing menial tasks. At both ends of the computing scale, this effectively means that business owners and server operators can delegate tasks to AI script, and can also ensure that systems can actively learn specific usage trends.
This means that, whether tweaking private networks or managing central servers, AI can effectively run clouds on its own basis – offering very little need for human intervention.
No need for maintenance
Whether PaaS / Platform As a Service or otherwise, a key element to this type of service is that it is immensely simplified. There is no need for the business owner to worry about learning new skills or processes, on top of actively providing a service.
Cloud providers assure end users that their servers, networking and storage solutions are managed by experts in the field. This means that there is also zero need to hire additional staff or to upskill team members to manage servers, networks or otherwise.
It is also worth remembering that with an off-site team ready to react, downtime in the face of unexpected power outages and more can decrease dramatically. Therefore, the SME (or larger) immediately saves money, and reduces the chance of losing business all the same.
Final statistics to keep in mind
If you run a business here and now, it’s highly likely you already have some familiarity with the cloud. Whether Dropbox, Microsoft Azure, the IBM Cloud or even Google Docs, its importance is prevalent across the ecosystem.
It’s estimated that more than 100ZB, or zettabytes, of available data will be available on the cloud. That’s one trillion GB – a truly staggering number – and we’re likely to hit this by mid-decade.
Finally, consider the average cost of data interruption, or breach, based on average statistics from 2020 alone. Companies lost $3.86 million, average cost per breach – and cloud technology can help to mitigate these costs from rising.
It’s time to embrace cloud computing
Despite the relative age of the technology, there is still abundant misinformation and a slowness to adopt cloud computing. However, the statistics are clear – we’re heading towards a more flexible, accessible and infinitely scalable future, along with the incredible potential for data we are building worldwide.
There are many, many further benefits to cloud computing worth exploring beyond this introductory guide. Moving into mid-decade, cloud standards will be the norm for start-ups, SMEs and corporations alike. As such, now is the time to consider setting up with leading expertise in cloud computing.